ISO 다운로드
- ubuntu-20.04.5-live-server-amd64 설치
https://old-releases.ubuntu.com/releases/20.04.5/ubuntu-20.04.5-live-server-amd64.iso
centOS 템플릿 복제해 m10 서버(IP: 211.183.3.10) 생성
ssh-server에 첫 접속할때 ‘yes’ 안물어보도록 하려면
1) ssh-client 설정파일( vi ~/.ssh/known_hosts )수정

# /etc/ssh/ssh_config 파일에서 위 내용을 no로 수정하고 주석을 해제하면 됨
2) 엔서블 옵션
--ssh-common-args="-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
앤서블 명령을 수행할때 이런 옵션을 주면 된다
- 퍼블릭키 넣어주기
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@211.183.3.10
- 인벤토리 생성
[root@control_node ans]# vi 0307.inven

[root@control_node ans]# ansible m10 -m ping -i 0307.inven --ssh-common-args="-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
[root@control_node ans]# vi ~/.ssh/known_hosts
# 여기에 없는 대상을 확인하고 물어보는게 StrictHostKeyChecking
# 이 파일의 211.183.3.10을 지우세요 = 한번도 접속 안한 상태로 돌아감

위에서 처럼 인자(옵션)를 계속 붙여줘도 괜찮고
인벤토리에 추가해줘도 괜찮다.
다시 [root@control_node ans]# vi ~/.ssh/known_hosts 의 211.183.3.10을 삭제하고

# 인벤토리에 위와 같이 구성

# 마찬가지로 yes를 묻지 않음
우분투 템플릿 생성
- 2 core, 2GB, 20GB, IP: 211.183.3.250/24



# 본딩(리눅스),티밍(윈도우) = 다수의 NIC 를 묶어주는 개념. 대역폭을 늘리거나 active-standby구조를 가져가고 싶을때







# 설치 후 user1로 로그인

# root 패스워드 설정후 root 계정으로 로그인
- ubuntu 20.04의 네트워크 설정 파일(IP 수정 가능)
root@ubun-tem:/home/user1# vi /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml
- ssh 루트 로그인을 허용하기 위해 설정 파일 수정
root@ubun-tem:/home/user1# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config

- 재시작
root@ubun-tem:/home/user1# systemctl restart sshd

# ubuntu에는 ufw라는 방화벽을 쓰는데, 기본적으로 비활성화 상태
이제 powershell로 id: root, pw: test123로 접근 가능
- 우분투 가급적이면 업데이트 잘해주자!
root@ubun-tem:~# apt update -y
root@ubun-tem:~# init 0
# 설정을 마친후 shutdown하여 앞으로 복제해서 쓰면된다.
- ip: 211.183.3.20/24, hostname: m20
m20으로 복제해서 우분투 서버 생성(Ubuntu iso 사용)
- vi /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml에서 IP 수정
root@ubun-tem:~# vi /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml

- 네트워크 설정값 반영, centos7의 systemctl restart network와 비슷
root@ubun-tem:~# netplan apply
debug 모듈
특정 변수의 값을 출력하거나, 메세지를 보여주는 모듈
ansible_facts = 대상 노드의 정보를 가져옴
ansible_facts가 활성화되어 있어야 debug 모듈을 쓸 수 있음
ansible_facts의 기본값이 원래 true기 때문에 굳이 false만 안하면 된다
- 플레이박스 생성
[root@control_node ans]# vi debug.yml
- name: debug_pb
hosts: m10
tasks:
- name: show_facts
debug:
var: ansible_facts
# 대상 노드의 ansible_facts라는 변수(앤서블이 지정해놓은 변수)의 값을 보여달라.
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook debug.yml -i 0307.inven
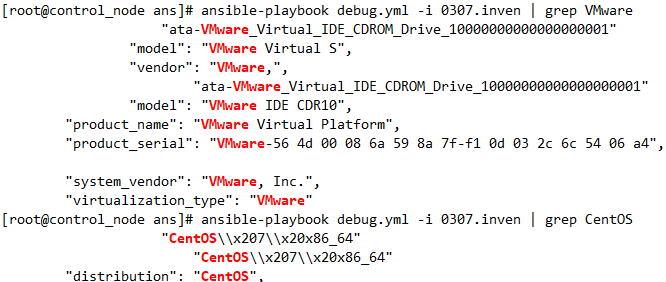
- name: debug_pb
hosts: m10
tasks:
- name: show_facts
debug:
var: ansible_distribution# ansible_facts를 ansible_distribution로 수정

register 모듈
모듈의 수행결과값을 변수에 저장하는 모듈
[root@control_node ans]# vi reg.yml
- name: register_pb
hosts: m10
tasks:
- name: ls_reg
shell: ls
register: ls_result # ls_result는word(내맘대로정하는변수)
- name: show_ls_result
debug:
var: ls_result


# 실제로 m10에서 ls를 치면 이렇게 출력
when 모듈
특정한 상황이 충족됐을때 모듈을 수행
ex. 만약에 리눅스 배포판이 CentOS면 yum을 통해 httpd를 설치하고, 배포판이 Ubuntu 인 경우엔 apt를 통해 nginx를 설치하고 싶을때.
- 배포판이 CentOS일때 httpd를 설치
[root@control_node ans]# vi when.yml
실습0)
위 when.yml을 start-when.yml로 복사후 web서버가 잘 동작하도록 만들고 접속이 잘되는지 테스트 해보세요.
- name: install_web_pb
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: install_httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
register: install_result1 # 여기에 변수로 저장
- name: start_httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
- name: show_result1
debug:
var: install_result1
- name: firewalld_stopped
service:
name: firewalld
state: stopped
enabled: false
- name: install_epel
yum:
name: epel-release
state: present
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook when.yml -i 0307.inven
실습1)
위 when.yml을 start-when.yml로 복사후 ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' 면 httpd 설치해서 동작시키고, ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'면 nginx를 설치하여 web서버가 잘 동작하도록 만들고 접속이 잘되는지 테스트 해보세요.
- 인벤토리 생성
[root@control_node ans]# vi 0307.inven
[m10]
211.183.3.10
[m10:vars]
ansible_ssh_common_args="-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
[m20]
211.183.3.20
[m20:vars]
ansible_ssh_common_args="-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
- 플레이박스 생성
[root@control_node ans]# vi when.yml
- name: install_web_pb
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: install_httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
register: install_result1 # 여기에 변수로 저장
- name: start_httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: true
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: show_result1
debug:
var: install_result1
- name: firewalld_stopped
service:
name: firewalld
state: stopped
enabled: false
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: install_epel
yum:
name: epel-release
state: present
when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS'
- name: install_nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'
- name: start_nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: true
when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu'
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook when.yml -i 0307.inven



풀이1)
| - name: setup for webserver hosts: web gather_facts: true become: true tasks: - name: httpd install yum: name: httpd state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' register: result - debug: var: result when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: httpd start service: name: httpd state: started enabled: yes when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' register: result - debug: var: result when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: nginx install apt: name: nginx state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' register: result - debug: var: result when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: nginx start service: name: nginx state: started enabled: yes when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' register: result - debug: var: result when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' |
# block 이라는 모듈을 통해 여러개의 모듈을 하나로 묶어줄 수 있으나, 그냥 하나하나 다 when 조건문으로 구성했다.
실습2)
하나의 플레이북에서 CentOS면 nfs-client, Ubuntu면 nfs-server로 nfs를 구성해보세요.
풀이2)
- nfs-server를 구성할 우분투에서는 nfs-kernel-server라는 패키지를 설치하면 된다.
- nfs-client를 구성할 CentOS에서는 셀리눅스와 방화벽을 꺼주면 될거다.
- 인벤토리 생성

[root@control_node ans]# vi nfs2.yml
| - name: Setup for NFS hosts: m tasks: - name: Install nfs-utils yum: name: nfs-utils state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: Install nfs-utils apt: name: nfs-kernel-server state: present when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: selinux disable selinux: state: disabled when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: stop firewall service: name: firewalld state: stopped enabled: false when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: make nfs_shared directory file: path: /shared state: directory mode: '0777' when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: configure /etc/exports lineinfile: path: /etc/exports line: "/shared *(rw,no_root_squash)" when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: nfs service restart service: name: nfs-server state: restarted when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' - name: make nfs_client directory file: path: /remote state: directory when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: mount directory mount: name: /remote src: 211.183.3.20:/shared fstype: nfs state: mounted when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' |
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook nfs2.yml -i 0307.inven
실습3)
CentOS의 경우 ssh 접속기록이 /var/log/secure 에 남는다. Ubuntu의 경우엔 /var/log/auth.log에 남는다. ssh log를 control node의 /root/log 디렉토리로 받아오는 플레이북을 만들어보세요. fetch 라는 모듈을 사용해서 해보세요.
풀이3)
| - name: send log hosts: m tasks: - name: fetch /var/log/secure fetch: src: /var/log/secure dest: /root/log/cent.log flat: yes when: ansible_distribution == 'CentOS' - name: fetch /var/log/auth.log fetch: src: /var/log/auth.log dest: /root/log/ubun.log flat: yes when: ansible_distribution == 'Ubuntu' |
handler
함수와 비슷
- 미리 내가 태스크를 정의해두고 호출(notify)해서 사용
- 변경사항이 발생했을때(changed) 트리거
ex. httpd가 설치되면 → 서비스 태스크를 호출해서 httpd 데몬을 동작
[root@control_node ans]# vi handler.yml
- name: handler_test_pb
hosts: cent
tasks:
- name: install_httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
notify:
- start_handler # 밑에서 이런 이름을 갖는 핸들러를 정의할 예정
handlers:
- name: start_handler
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
enabled: yes

[root@control_node ans]# vi 0307.inven

- m10에 httpd가 이미 설치되어있다면 제거
[root@m10 ~]# yum remove httpd



실습)
새로 ubuntu 템플릿 하나 복제해서 211.183.3.30(m30)으로 만드세요. m30에서 웹서버가 동작하고 있습니다. 해당 서버로 파일이 복사되어 index.html 파일에 변경사항이 생겼을때 웹서버를 재시작 시키는 플레이북을 한번 만들어보세요.
- vi /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml에서 IP 수정
root@ubun-tem:~# vi /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml

- 네트워크 설정값 반영, centos7의 systemctl restart network와 비슷
root@ubun-tem:~# netplan apply
- 퍼블릭 키 부여
[root@control_node ans]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@211.183.3.30
- 인벤토리 내용 추가
[root@control_node ans]# vi 0307.inven
[m30]
211.183.3.30
[m30:vars]
ansible_ssh_common_args="-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
- 테스트 파일 생성
[root@control_node ans]# echo test > test.html
- 플레이박스 생성
[root@control_node ans]# vi form30.yml
- name: form30_pb
hosts: m30
tasks:
- name: Install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: Start nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: started
enabled: true
- name: Copy index.html to web server
copy:
src: test.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
notify: Restart nginx # 파일 변경 시 핸들러 실행
handlers:
- name: Restart nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: restarted
- 플레이박스 실행
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook form30.yml -i 0307.inven
- 내용 확인
[root@control_node ans]# curl 211.183.3.30


풀이)

[root@control_node ans]# vi han-copy.yml
| - name: play_handler_pb hosts: m30 tasks: - name: install_nginx apt: name: nginx state: present - name: start_nginx service: name: nginx state: restarted enabled: yes - name: copy_index copy: src: test.html dest: /var/www/html/index.html notify: - restart_handler handler: - name: restart_handler service: name: nginx state: restarted |
- 플레이북과 동일한 경로에 test.html 생성
[root@control_node ans]# echo test > test.html
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook form30.yml -i 0307.inven
[root@control_node ans]# curl 211.183.3.30
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook han-copy.yml -i 0307.inven
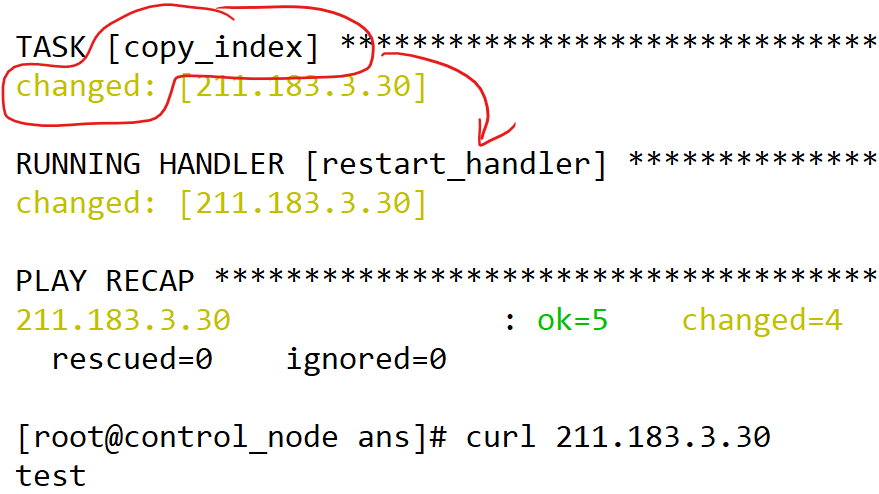
# 첫 실행시 잘 동작

# 두번째 동작시 핸들러 미실행
[root@control_node ans]# echo test111 > test.htm
[root@control_node ans]# ansible-playbook han-copy.yml -i 0307.inven
# test.html 파일을 수정후 플레이북을 재실행하면 copy 태스크가 changed가 될것이다.

# copy 태스크에 변경사항이 생겨서 핸들러가 동작했다.

'AWS Cloud School 8기 > Ansible' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 46일차) 2025-03-06(Ansible node, 모듈, 멱등성) (0) | 2025.03.06 |
|---|---|
| 45일차) 2025-03-05(Ansible, cent-tem, 클론 템플릿 생성) (0) | 2025.03.05 |
